使用定制标签库使得JSP程序更加简洁、可读性和可维护性大大的提高了。因此JSP定制标签的优势是非常明显的,它被认为是JSP所有特性中最被看好的特性。
我们要编写一个标签,向请求者的浏览器输出”Hello World!”,同时该标签是一个没有体内容的空标签。
JSTL 库安装(如果你的编译器是netbeans,可以直接从自带的库中加载)
- 从Apache的标准标签库中下载的二进包(jakarta-taglibs-standard-current.zip)。
官方下载地址 - 下载jakarta-taglibs-standard-1.1.2.zip 包并解压,将jakarta-taglibs-standard-1.1.2/lib/下的两个jar文件添加到你项目的库。
- 编写标签处理器.
创建一个名为HelloWorldTag 的java类
package Tag;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.TagSupport;
/**
*
* @author YU
*/
public class HelloWorldTag extends TagSupport {
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
try {
pageContext.getOut().print("Hello World!");
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new JspException(ioe.getMessage());
}
return SKIP_BODY;
}
}
重新实现doStartTag方法:实例代码将定制标签的功能在doStartTag方法中实现。由于这个标签是一个空标签,在doEndTag方法中实现定制标签的功能也是完全相同的结果。
pageContext对象是JSP处理器通过调用标签的setPageContext()方法将JSP页面的pageContext对象传递给标签的。标签需要通过pageContext对象获得对JSP页面的out对象的引用,以便向客户端输出信息。
因为我们的示例定制标签是一个空标签,没有体内容需要处理,因此doStart()方法应当返回SKIP_BODY,向JSP处理器表示无需对标签的体内容进行处理。
- 编写标签库描述文件 TLD文件负责向JSP引擎描述标签库的版本要求、可用标签的数量和名称、各标签的标签处理器类等信息。
在此,我们需要为每一个标签建立一个元素,该元素描述了标签的引用名、处理器类名、体内容说明等重要信息。
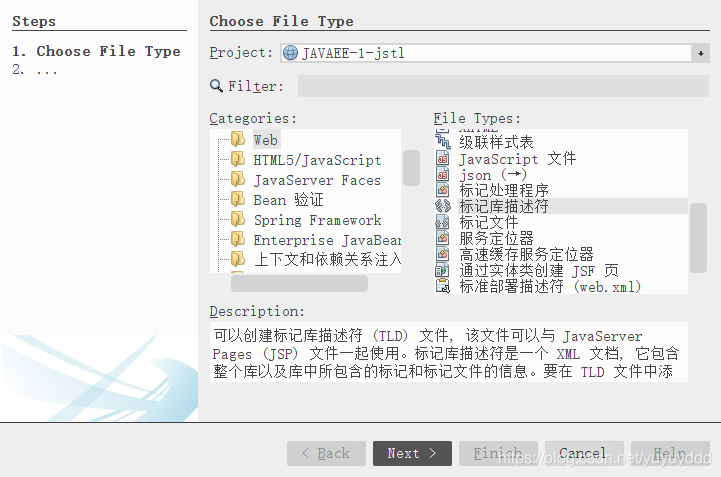
在WEB-INF/tlds新建一个标记库描述符 mytags.tld
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<taglib version="2.1" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_1.xsd">
<tlib-version>1.0</tlib-version>
<short-name>mytags</short-name>
<uri>/WEB-INF/tlds/mytags</uri>
<tag>
<name>HelloWorldTag</name>
<description> This tag will output string "Hello World!" </description>
<tag-class>Tag.HelloWorldTag</tag-class>
<body-content>empty</body-content>
</tag>
</taglib>- 部署标签库
我们需要在要使用HelloworldTag标签的Web应用程序的web.xml文件声明对该标签的TLD引用。在此之前,需要将标签的标签处理器放置到Web服务器能够找到的地方。这里与实现标签相关的文件有HelloworldTag.class文件和hello.tld。例如,对于Tomcat服务器,把标签处理器类文件放置到/WEB-INF/classes目录下,把hello.tld文件放置到/WEB-INF目录下。
然后需要在web.xml文件中加入对标签库描述文件的引用,这样web应用程序就能够使用定制标签:
在WEB-INF下新建一个标准部署描述符:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<jsp-config>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>http://www.test.com/jst/core</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/tlds/mytags.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
</jsp-config>
<session-config>
<session-timeout>
30
</session-timeout>
</session-config>
</web-app>
<taglib>元素只不过是利用<taglib-uri>和<taglib-location>在引用URI和TLD文件的物理地址之间做了一个简单的映射而已 ,<taglib-uri>表示当JSP页面使用标签库时,要按指定的URI引用。
- 在JSP中导入和使用标签库
<%-- Document : Hello Created on : 2019-4-9, 19:49:23 Author : YU --%> <%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <%@taglib uri="http://www.test.com/jst/core" prefix="mytags"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Tag Page</title> </head> <body> <mytags:HelloWorld/> </body> </html>
运行可以看到结果:
其实可以跳过第三步配置web.xml,不声明对标签的TLD引用,如果这样子做,那么在JSP中导入的uri应为“/WEB-INF/tlds/mytags.tld”
建议配置web.xml,这样做的好处是:当我们修改或改动实际路径是,不用修改代码的路径,这样方便可用。
有几个地方需要注意一下
- 在JSP使用标签库的时候务必要导入<%@ taglib prefix=”c” uri=”http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>,否则可能会报错。
- 标签库描述文件涉及到的名字,如tag-class需要和对应的标签处理器类的名称一样。
编写一个简单的带有属性的定制标签
编写一个简单的带有属性的定制标签myFont,能够根据标签设定的属性显示不同形式的文字。
- 编写标签处理器MyFont.class
为了给自定义标签添加属性,可在标签处理器类的定义中利用和JavaBean类似的机制来进行属性的定义。
特殊之处是,标签的属性通常是JSP页面用来设置的。因此标签的属性在实现上通常只有set方法。package Tag; import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException; import javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter; import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.TagSupport; /** * * @author YU */ public class MyFont extends TagSupport { private String color = "#000000"; //默认情况下字体为黑色 private String bgColor = "#ffffff "; //默认情况下背景色为白色 private String borderColor = "#000000"; //默认情况下文字边框为黑色 private String align = "CENTER"; //默认情况下文字居中 private String fontSize = "3"; //默认情况下字体大小为3 private String border = "0"; //默认情况下表格无边 private String width = null; //默认情况下表格宽度由文字长度确定 public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public void setAlign(String align) { this.align = align; } public void setFontSize(String fontSize) { this.fontSize = fontSize; } public void setBorder(String border) { this.border = border; } public void setWidth(String width) { this.width = width; } public void setBorderColor(String borderColor) { this.borderColor = borderColor; } public void setBgColor(String bgColor) { this.bgColor = bgColor; } public int doStartTag() throws JspException { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); try { JspWriter out = pageContext.getOut(); sb.append("<table "); if (border != null) { sb.append(" border=\"" + border + "\""); } if (borderColor != null) { sb.append(" bordercolor=\"" + borderColor + "\""); } if (width != null) { sb.append(" width=\"" + width + "\" "); } sb.append("><tr><td "); if (bgColor != null) { sb.append(" bgcolor=\"" + bgColor + "\" "); } if (align != null) { sb.append(" align=\"" + align + "\""); } if (borderColor != null) { sb.append(" bordercolor=\"" + borderColor + "\""); } sb.append("><font size=\"" + fontSize + "\" "); sb.append(" color= \"" + color + "\" >"); out.print(sb.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new JspException(e.getMessage()); } return this.EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE; } public int doEndTag() throws javax.servlet.jsp.JspException { try { JspWriter out = pageContext.getOut(); out.print("</font></td></tr></table>"); } catch (Exception e) { throw new JspException(e.getMessage()); } return this.EVAL_PAGE; } }
这些setXXX方法将在doStartTag方法之前由JSP引擎调用。因此,在doStartTag及其后续方法中,可认为color、bgColor等字段值是已赋值的。但是,未出现在JSP标签中的属性值将保持其原有值。
doEndTag方法的主要工作就是收尾。在本例中,JSP引擎在遇到</MyTag:Font>时调用本方法,而本方法将在页面中输出</td></tr></table>以闭合表格。
doEndTag方法返回时,意味着自定义标签处理器的工作结束。在结束前,标签处理器可以指示JSP引擎是否继续处理其余页面。当返回EVAL_PAGE,则JSP需要继续处理其余页面;若返回SKIP_PAGE,JSP引擎将忽略标签后的页面内容。
编写标签库描述文件
<tag> <name>MyFont</name> <description>Display different forms of text</description> <tag-class>Tag.MyFont</tag-class> <body-content>jsp</body-content> <attribute> <name>color</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>bgColor</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>borderColor</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>align</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>fontSize</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>border</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> <attribute> <name>width</name> <required>false</required> </attribute> </tag>每个标签属性都需要用一个attribute子元素进行说明。name定义了在JSP页面中的属性名,required说明了该属性是否是必需的.
部署标签库
因为我是在同一个写的两个jstl标签,所以制作上一个标签时已经部署了。在JSP中导入和使用标签库
<%-- Document : Hello Created on : 2019-4-9, 19:49:23 Author : YU --%> <%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <%@taglib uri="http://www.test.com/jst/core" prefix="mytags"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Tag Page</title> </head> <body> <mytags:HelloWorld/> <mytags:MyFont border="1" borderColor="#000000" bgColor="#00ff00" fontSize="5" color="#ff0000"> hello myFont! </mytags:MyFont> </body> </html>
运行效果:



